Chapter Seven:Measuring SEO Success
Establishing a baseline of your website’s performance is essential for understanding the effectiveness of your digital marketing efforts.
To get started, determine which metrics are most important for your business and make sure you have an appropriate tracking system in place.
With a proper measurement system, you can avoid the frustrations of incomplete data, or hindrances from an unclear picture of what is (or is not) working for your business.
In this chapter, we’ll look at setting the foundation for tracking your online marketing efforts, along with some important metrics to analyze regarding local SEO.
Setting the stage for success starts with being able to measure progress. Thankfully, getting started with analytics is free and easy to set up.
Analytics Tools
Google Analytics
What is Google Analytics (GA)?
The industry standard web analytics platform that tracks and reports data about your website. Using Google analytics properly will help you measure traffic, consumer engagement, campaigns and conversions.
Why You Need Google Analytics?
If you have a website and are interested in improving its performance, then you need Google Analytics. This free software is an entryway into understanding your website, and how to leverage its performance to grow your business.
What Information Does Google Analytics Provide?
Google analytics provides a wealth of information about your website and its visitors. Analytics can help answer many questions to improve your site’s performance like:
- How many people are visiting my site?
- Which pages of my site are most popular?
- Where are my users located?
- What types of traffic are most profitable?
- What sites are referring traffic to my site?
- How often do visitors return to my site?
- What kind of devices are visitors using to access my site?
These are some basic questions that Google Analytics can answer, but when you really start digging into the data, you’ll find it’s capable of much more!
Google Search Console
Google Search Console helps you review how well your site is performing in Google Search. It provides insights on how Google is reading your site, while making suggestions and notifying you of any issues or errors that it finds.
Search Console provides a host of helpful features, namely checking how many web pages are indexing, finding links pointing to your site, identifying popular landing pages, pinpointing queries your site is indexing for and more. Search Console is also the platform you use to submit updated sitemaps and request indexing of recently published pages.
This tool is great for checking site errors, search analytics and site health audits.
Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing Webmaster Tools (BWT) is Bing’s counterpart to Search Console, providing detailed insights about how your website performs in Bing search.
This tool helps local business owners identify and understand existing problems that their site may have. Using this tool on a regular basis will help identify errors that need to be fixed along with suggestions to better optimize your web pages for Bing search.
BWT grants access to similar reports that you would find in Search Console, including search queries, impressions and a list of backlinks to your site.
Setting up Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a robust analytics tool that offers valuable insights about your website’s performance and is quick to setup. Once you create an account and add a snippet of code to your site, Google will begin tracking information about where your traffic is coming from, what pages users are interacting with and how long people are staying on your site.
To get started with Analytics you will first need a Google Account. After creating an account, you can visit analytics.google.com to sign up.
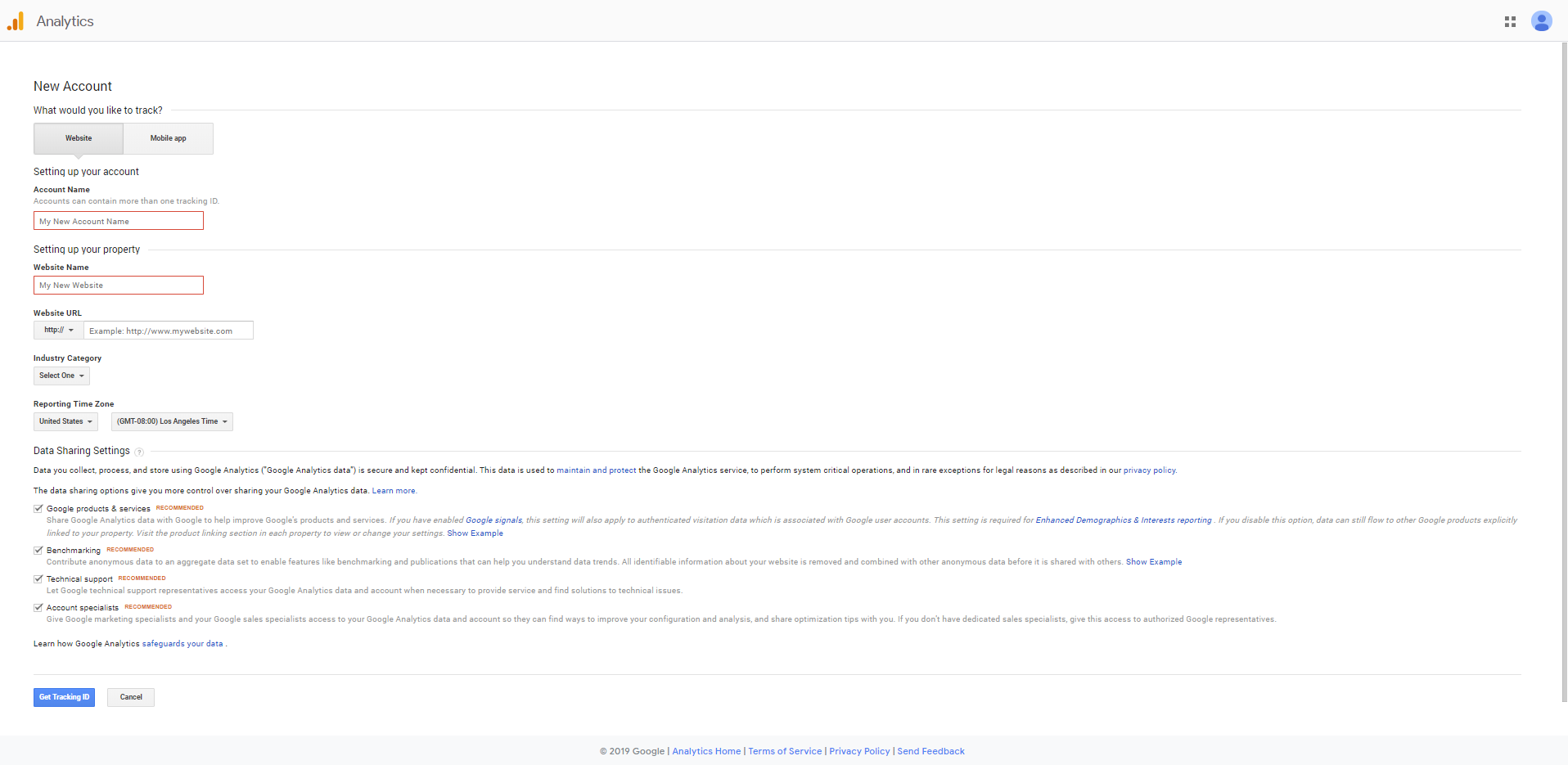
- Account Name: Enter your business name or the name of your parent company. If you have multiple businesses, keeping an organized account structure will make life much easier as you rely on this data to help you make future marketing decisions.
- Website Name: Enter the name of your website.
- Website URL: Enter the URL of your website (www.examplebusinessurl.com).
- Industry Category: Select an industry category that represents your business. This allows for more tailored reporting.
- Reporting Time Zone: Select the appropriate time zone for accurate reporting based on your geographical location.
- Select which data (if any) you would like to share with Google.

Create Additional Views
By default, Analytics will create an “All Web Site Data” view, which serves as a ‘raw’ view that contains unfiltered data.
Creating additional views within Google Analytics allows you to filter unwanted traffic. For our basic setup, we will create two additional views: ‘Filtered’ and ‘Sandbox.’
- The Filtered view will block unwanted traffic sources from skewing our data.
- The Sandbox view will serve as a test view to experiment in the future.
Adding a View
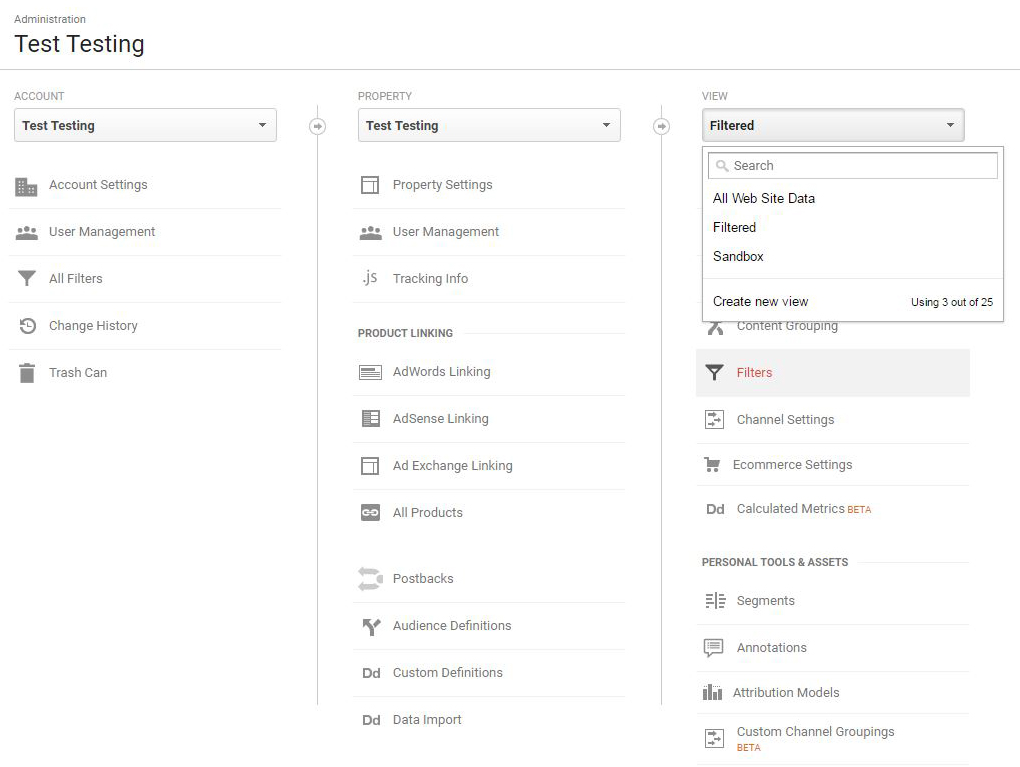
Navigate to: Admin » Views Column Drop Down » Create New View.
Create two new views, named “Filtered” and “Sandbox.”
Adding a Filter
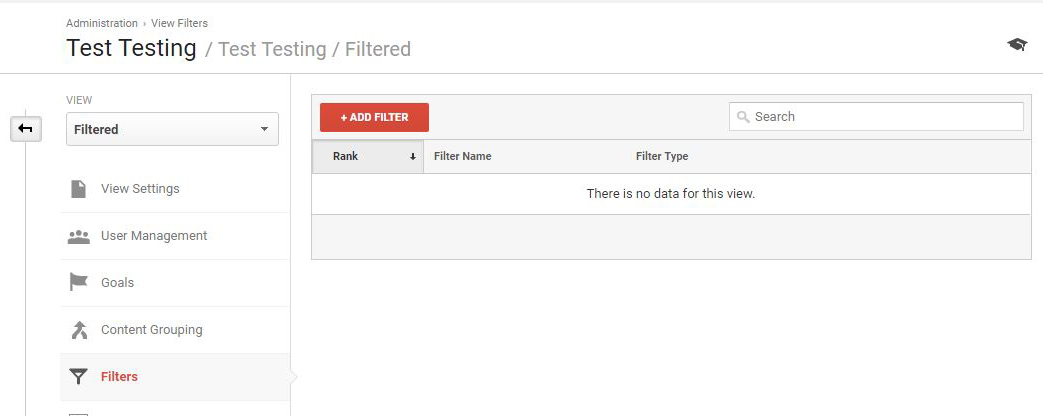
- In the Filtered View, select Filters.
- Click “+Add Filter.”
- Then enter a filter name.
- Select predefined filter type.
- Exclude » Traffic from the IP addresses » that are equal to
- Enter your IP address.
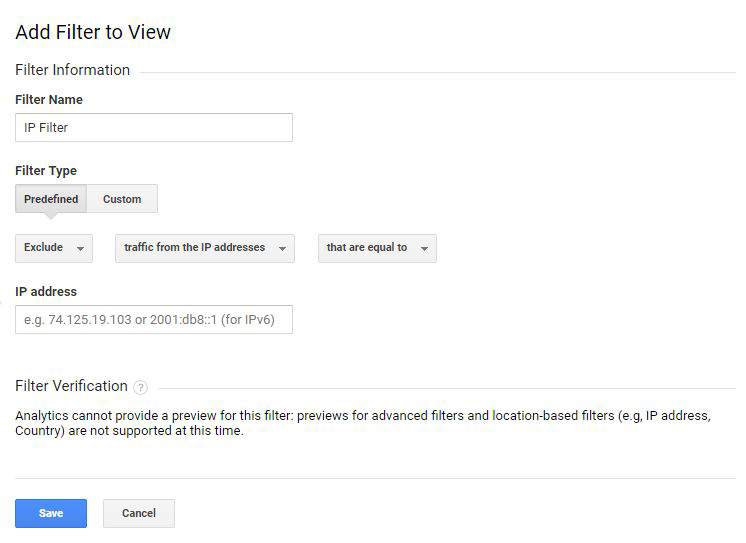
If you are unsure of your IP address, you can Google search “what is my IP” to find out.
Now that setup is complete, we are ready to implement Google Analytics on the website.
How to Install GA Tracking Script
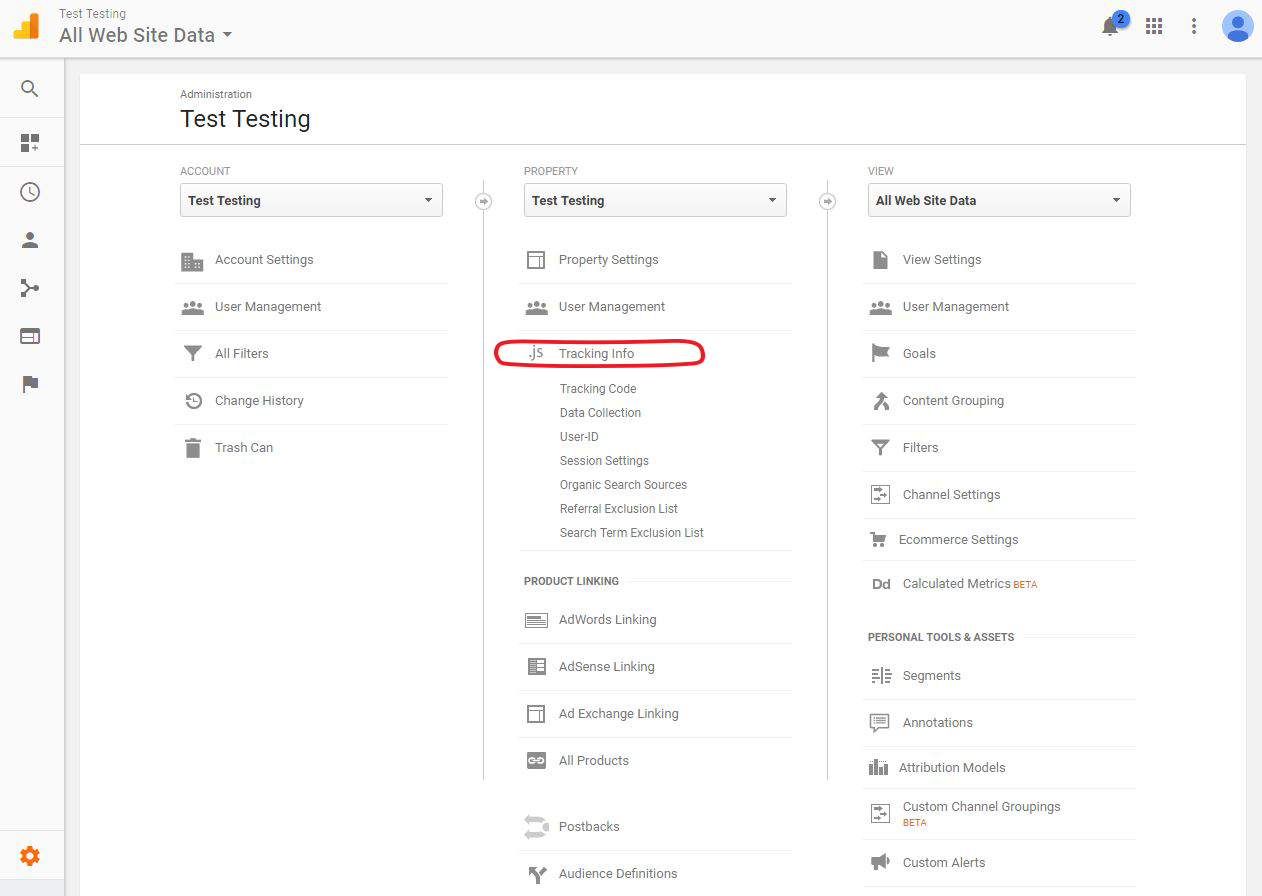
Navigate to your Tracking ID: Admin » Tracking Info » Tracking Code
This code must be installed on every page of your website. The installation method will vary depending on the type of website you have (WordPress, Shopify, Squarespace). Here, we’ll look at WordPress installation.
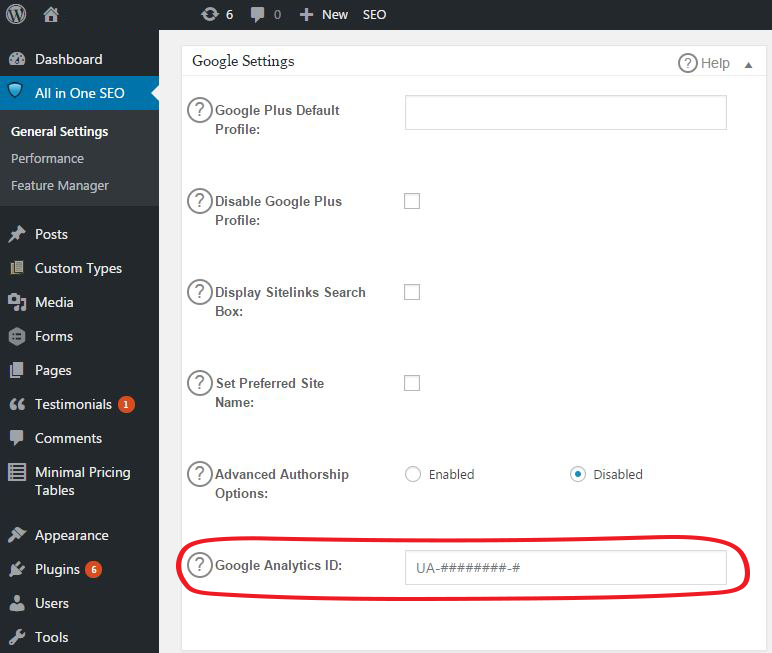
Plugins, like All in One SEO, make installing Google Analytics on your site a breeze. After installing the All in One SEO Plugin, navigate to the Google Settings section, and enter your unique UA code.
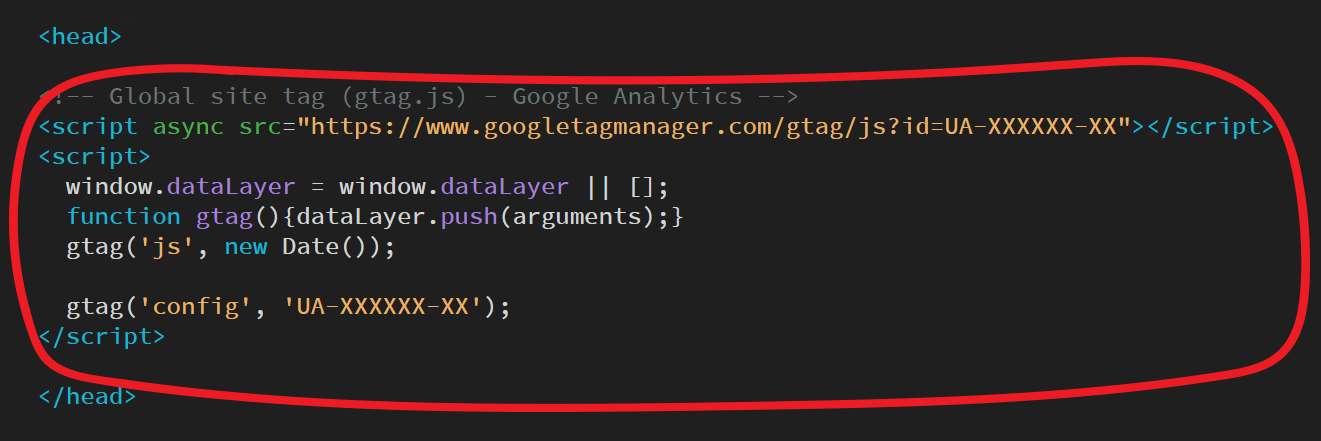
If your site is using FTP, or you elect to not use a plugin, you can enter the full JavaScript snippet into the <head> section of your site.
Verify That Analytics is Tracking
After your Analytics code is on your site, you must check to ensure the code is accurately tracking visitors to your site. You can quickly do this by checking real-time tracking within Google Analytics.
Real-Time » Overview
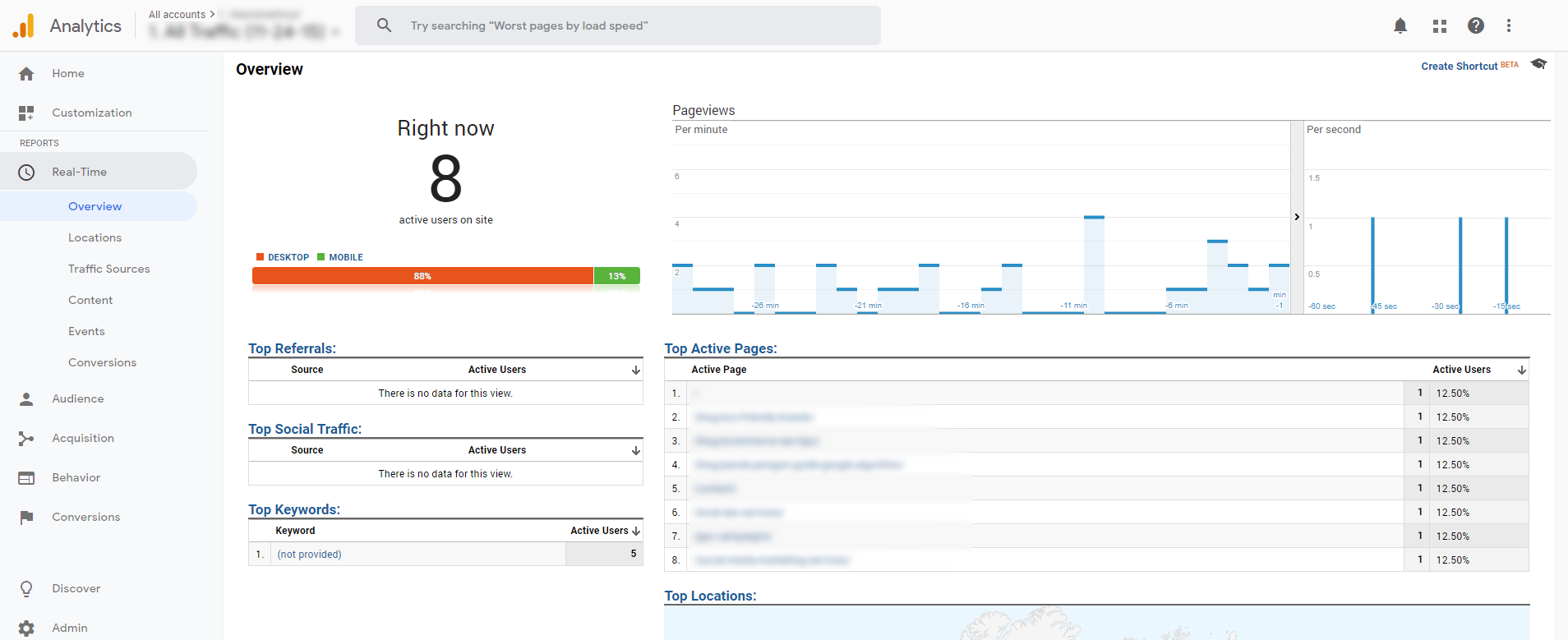
Navigate to a few pages to make sure Analytics is tracking. Another friendly tool to check your entire site for the Analytics code is gachecker.com. This website will scan your site and notify you of all pages that are missing the Analytics tracking code.
In a standard Analytics account, the data takes roughly 24 hours to display within reports. So, check back the next day to ensure your data has populated in all three of the views we created.
Creating Goals
To measure tangible business metrics like leads, signups or downloads, you need to configure goals within your Analytics account.
In Google Analytics, you have 4 ways of tracking goals:
- Destination URLs: Used to track when someone reaches a specific page
- Duration: Used to track how long someone stays on your website
- Pages/Screens per Session: Used to track the number of pages someone views
- Events: Used to track custom interactions of things like button clicks or video views
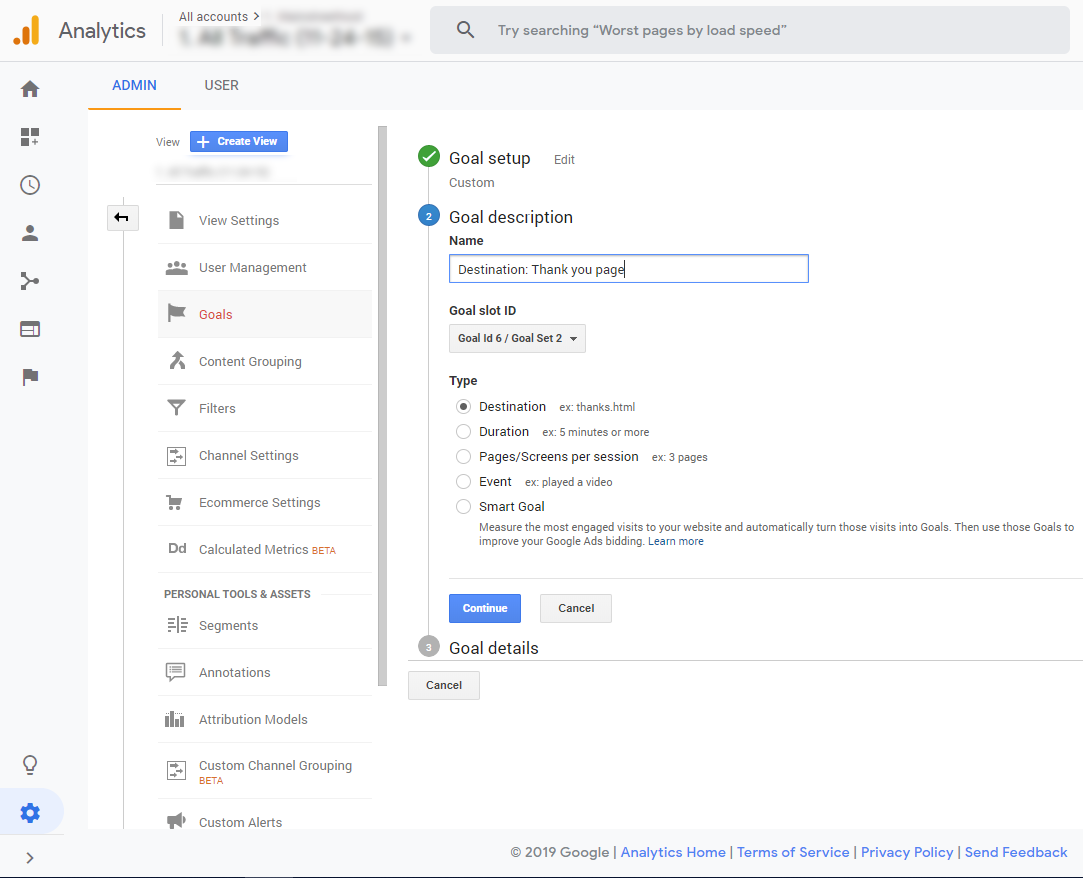
For this example, we will look at creating a destination URL goal, which is ideal when you use a thank you after a conversion.
- Log in to Google Analytics
- Click on “Admin” in the bottom right
- Select “Goals” under the view column
- Click “+ New Goal”
- Choose “Custom” and click “Continue”
- Enter a name for your goal
- Select the destination radio button and click “Continue”
- Enter your thank you page URL
- Click “Save”
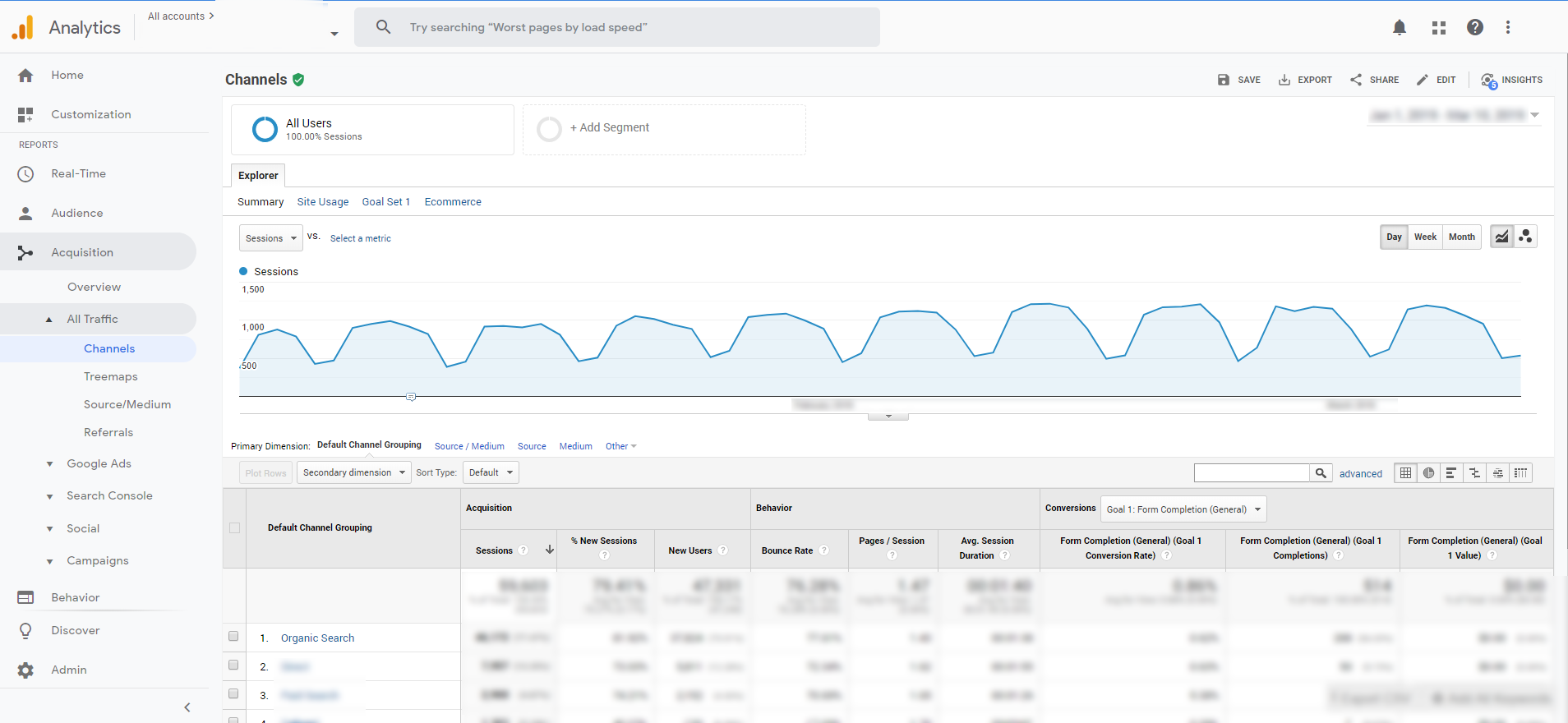
Measuring Organic Traffic
Google Analytics allows you to quickly measure the success of your local SEO efforts by looking at your organic (search engine) traffic growth.
In Google Analytics, go to: Acquisition » All Traffic » Channels
Then click on “Organic Search”
Summary
Tracking the performance of your optimization efforts is essential for the success of local SEO.
By monitoring analytics, you’ll be able to use tangible data to refine your local strategy.
Compare your results with previous periods - focusing on growth month-over-month, quarter-over-quarter and year-over-year.

