Website traffic is the number of visits a website receives in a given time period. Naturally, any website is looking to get a steady pool of visitors and consistently grow. More than that, businesses are competing for not just any traffic but targeted traffic that can bring them qualified leads and loyal customers.
Understanding where visits come from and how to check website traffic is an integral part of any digital marketing and SEO strategy. In this post, we’ll look at major traffic sources, how they differ from each other, and how to get the most out of each of them.
Six Major Website Traffic Sources
You might want to get clicks from various channels: from search to ads and from social media to personal recommendations. All the sources require separate efforts and you need to understand which of them work for your business and which are the most important to focus on.
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic means getting clicks from search. To attract users looking for answers on Google or another search engine, you’ll have to make it to the top 10 results (the results on the second page get a CTR of less than 1%) and make your page stand out among all others. SEO should be your most consistent investment as it is responsible for more than half of all traffic.
Pros of organic search:
- This source of traffic significantly outperforms all others
- It offers durable results
- Its opportunities are endless: there’s no limit to how many pages and for how many keywords you can get ranked in search
- You can do SEO on a small budget
Cons of organic search:
- It takes time for your SEO efforts to pay off
- There are many aspects to take care of and different specialists to involve (SEOs, developers, content marketers and copywriters, etc.)
How to increase website traffic from organic search:
- You need to start from building an SEO strategy and the number one task here is keyword research. You might need a keyword tool with a huge database to find what queries users type to find your competitors and information relevant to your business. After collecting a website’s keyword list, filter all your queries to have manageable groups divided by search intent, formulation, specification, or any other criterion.
- Analyzing the competition is also a part of SEO basics. Find out what pages of competitive domains are top performing in search for your target keywords and visit them to get the idea of why they are ranking high and how you can do better.
- Helpful and relevant content is the most important ranking factor. Put all the insights from keyword and competitor research into your landing pages, blog posts, and other pieces of content—make sure that your webpages are authoritative and easily readable. Consistency is also important: for instance, websites that publish more than 16 blog posts per month have 3.5X higher chances of getting traffic than those that publish 4 or less.
- Links are another top important factor for earning search engine rankings. Build a solid backlink profile by finding high-quality domains and making them link out to your pages. This is possible when you have a developed brand and exceptional content which other people want to share.
- All of the above falls short if you don’t take care of technical SEO. Secure your site with the latest protocol and encryption, make all your important pages easily accessible for search bots, and optimize page experience factors so that it doesn’t take long for your content to load and become interactive.
Paid Traffic
Paid traffic means visitors that come from advertising like Google Ads or Facebook Ads. Unlike other sources, paid traffic comes at a certain price and the more you pay, the more likely you are to win new customers. Naturally, you also have expenditures while working on other traffic channels, when hiring specialists, purchasing tools, etc. But with paid traffic, you’re paying exactly for publishing your content and getting it seen by your target audience.
Pros of paid traffic:
- You can reap the benefits really fast and can start getting clicks the same day you launch the ads
- It allows for precise targeting: you can set the exact demographics to get your ad shown to and receive highly qualified traffic as a result
Cons of paid traffic:
- Its results are temporary
- It is expensive: a monthly PPC spend can exceed $10,000 even for small and medium-sized businesses
How to maximize paid traffic:
- Decide which advertising platforms work best for your business.
- Create an advertising strategy involving PPC ads, social media ads, and display ads (if these types work for your business). Develop your campaigns with regard to each medium: for example, with PPC, you can target exact search intents, while with Facebook ads, you can target exact demographics.
- Regularly review your keyword list and segment it to create more effective PPC ads based on groups of keywords.
- Use ad extensions to better structure your ads and make them more appealing.
- Make sure your landing pages are relevant to your ads. If they don’t match, you won’t get the desired traffic.
Email Traffic
Email traffic means users were brought to your website from your email marketing efforts. When sending information about your services, news, or promotions to your customers and leads, you need to make sure that they open the emails, read them, and follow the links. To do so, you need to grab attention in the subject line and keep the emails informative, engaging, and personalized.
Pros of email marketing:
- This traffic source has the highest ROI ($38 on every $1 spent on average)
- It helps build trust and loyalty with customers
Cons of email marketing:
- It’s hard at the beginning when you have to collect an email list
- It takes a lot of effort to segment the audience you want to send emails to and experiment with what schedules and tactics work best
How to grow email traffic:
- Consistently grow your email list and make sure that your website offers an opportunity to subscribe whenever it’s relevant. Working on each email, segment your list according to the stages in the sales funnel or another criterion to provide people with the most helpful content.
- Craft personalized messages in the emails and make your CTAs clear (use action words and buttons to make them more attractive).
- Design emails so that they look beautiful and function properly on any device and screen resolution. 41% of emails are opened on mobile devices so you should keep your design mobile-first.
- Experiment with frequency and be consistent in your email communication.
Social Media Traffic
Social media traffic is users from social networks. As an important part of inbound marketing, social media helps gain prospects by engaging with the audience through the content.
Pros of social media:
- It allows for direct communication with the audience and increasing loyalty to your brand and to what you’re offering
- It helps build a website’s authority
Cons of social media:
- Social networks are unpredictable and content may get viral for no justifiable reason
- A lot of social media traffic is left untracked: when users share links to websites using their social accounts, it comes as an undefined source of traffic
How to boost traffic from social media:
- Develop a publishing schedule with regard to each platform’s nature. For example, it’s advisable to tweet 5 times a day and post on LinkedIn 2-5 times a week.
- Make your posts as engaging as possible. Use visuals, ask questions, and make the very beginning of each post intriguing.
- Automate when it makes sense. There are lots of social media automation tools that allow scheduling posts and getting your message seen at the right time across many platforms.
Referral Traffic
Referral traffic means visits from other websites. Getting sources to refer to you and place your links in their content relies on link building practices and PR activities. It can be a paid partnership or earned, free publicity—either way, having links to your website on external sources establishes your credibility and boosts traffic.
Pros of referral marketing:
- It expands your reach for the target audience (when the links are placed relevantly)
- It has lots of free opportunities to grow traffic
- It opens up new connections and facilitates relations with media, influencers, affiliates, etc.
Cons of referral marketing:
- There might be speculative link placements so you have to monitor if low-quality or irrelevant websites refer to you
- You have no control over who sees and follow your links
How to generate referrals:
- Submit your business to relevant listings and directories.
- Research opportunities to get mentioned on review platforms: reach out to websites that review businesses in your niche, encourage your customers to leave feedback on review and rating platforms.
- Contribute to authoritative sources to share expertise and mention your website in a natural way.
- Cooperate with industry experts and influencers for them to get to know about your website and share their opinion through their channels.
Direct Traffic
Direct traffic means those visits when people know a website they need and type its address in their browser. Some other types of visits are also categorized as direct traffic in Google Analytics: clicks from bookmarks; clicks from files, apps, or QR codes; clicks from text or chat messages; clicks from campaigns with an inaccurate tracking code, etc. To earn direct website visits, you have to put consistent efforts into all of the traffic channels: work on SEO, launch ad campaigns, run social media accounts, send emails, and cooperate with referring sources.
Pros of direct traffic:
- It’s an indicator of earned visitors
Cons of direct traffic:
- It creates tracking issues as Google Analytics includes undefined sources of traffic in this category
Important Traffic Metrics
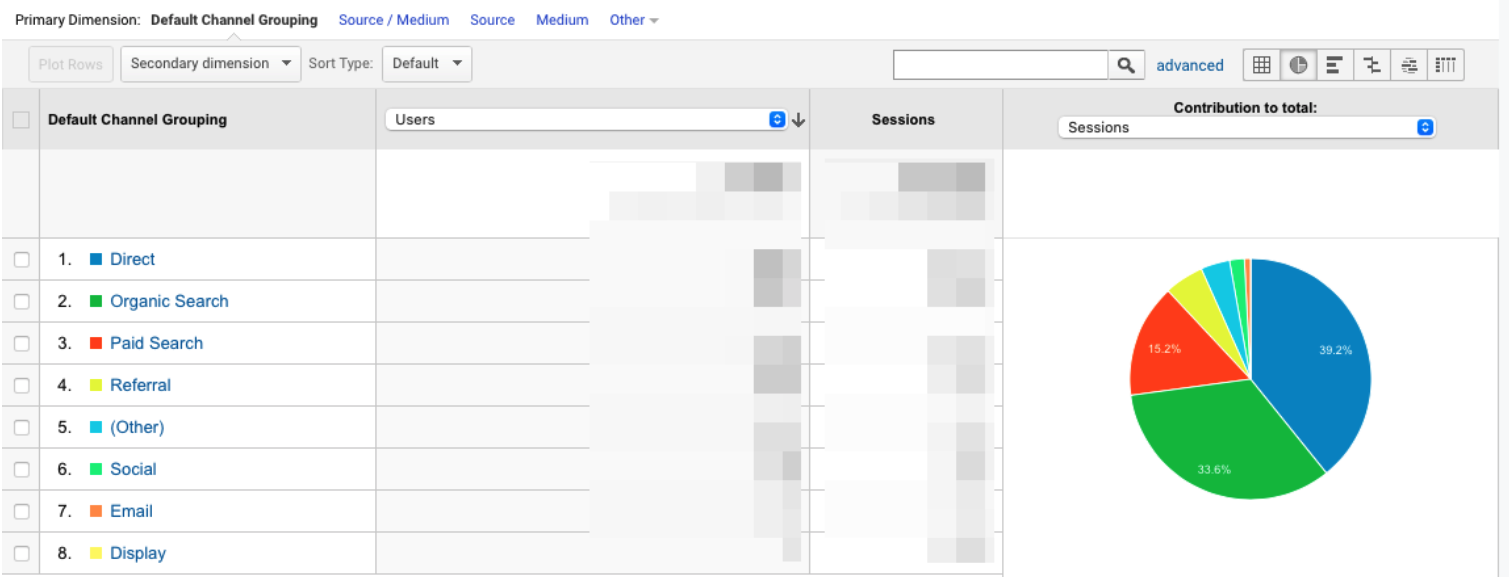
Besides knowing the differences between traffic sources and the methods of benefiting from them, you need to know how to track your website visits. Here’s the list of the metrics you’ll see in Google Analytics:
- Users and new users: the number of all unique visitors and first-time visitors in a given period of time
- Sessions: the number of visits including both new and returning visitors (100 visits of the same person will count as 1 unique visitor but 100 separate sessions)
- Source and medium: where the user comes from, with source indicating a particular traffic channel and medium indicating its general category (for example, Google is the source and CPC the medium)
- Bounce rate: the percentage of visitors who don’t stay on a website but leave it after visiting one page
- Average time on a page and session duration: the first metric shows how much time users spend on each particular page and the second metric shows how much it takes for users to perform a particular action on a website
- Events and goals: events are specific actions other than pageviews and event goals are the desired outcomes that you want to track (downloads, registrations, etc.)
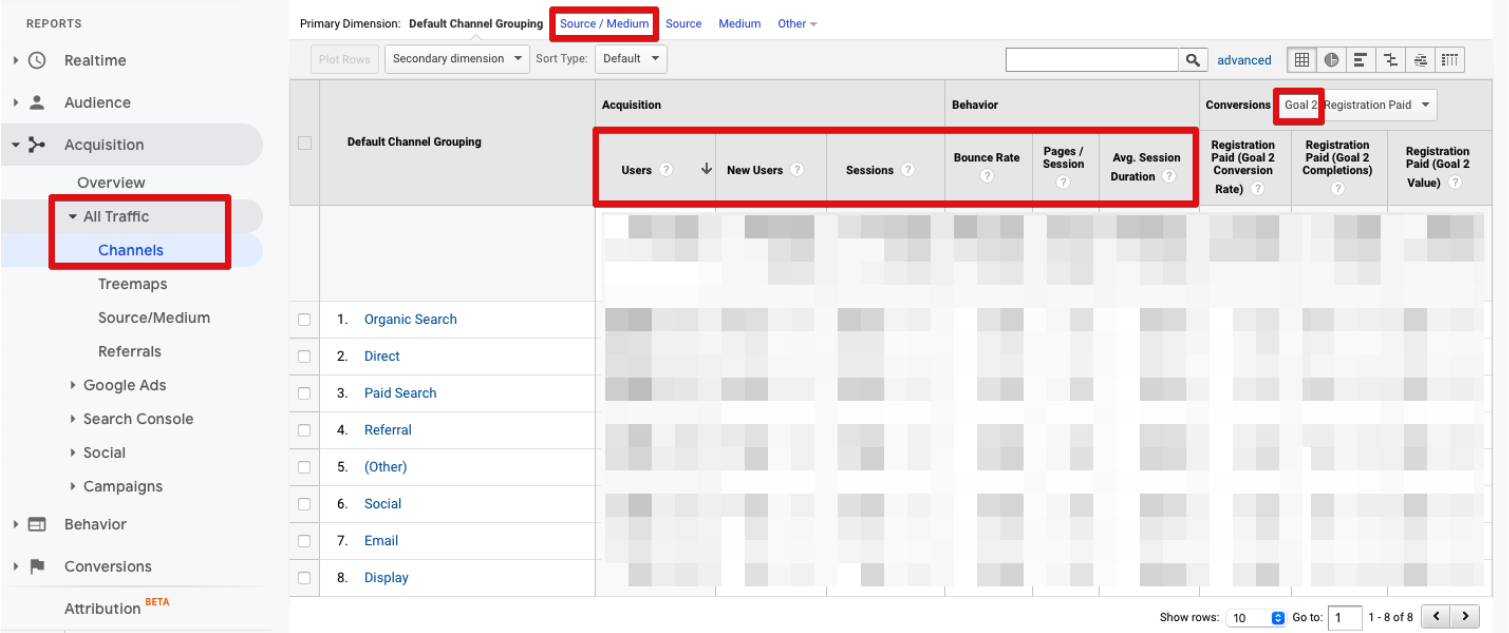
Apart from these metrics, you can monitor lots of parameters regarding your visitors:
- Demographics: age and gender
- Interests: categories and market segments visitors are interested in
- Geo: language version of the website and user locations
- Technology: devices, operating systems, screen resolutions, etc.
Monitoring traffic metrics with regard to your conversion goals and learning more about your visitors will help you improve all promotion-related activities and gain more clicks and interactions. You should always understand what is website traffic from each particular source and how to measure your results across various channels.
Increase Your Website Traffic by Leveraging All Sources
Making your business known and discussed, increasing the number of website visitors and customers are tightly connected. To grow your traffic, you have to work on all potential sources and engage in activities that pay off in both the short and long run. Expand your exposure by optimizing your website for search, creating paid ad campaigns, as well as working with social media, emails, and referrals.
Most importantly, continuously analyze your sources and spikes in traffic to define what approaches are most successful and what potential markets there are to explore. Get a Google Analytics report on traffic emailed to you so that you never miss a thing and stay on track with your traffic strategy.